New Expunction Laws on the Horizon – Second Chance Act
Monday, June 15th, 2020
In December of 2017, the accessibility of the expunction process had been drastically improved by Senate Bill 445, and now we are looking at even more changes to become effective December 1, 2020 lifting previous requirements, and allowing for a second chance in even more scenarios. Below are a few examples of the revisions to the expunctions laws applicable to offenses committed by persons age 18 or older:
- In addition to felonies and misdemeanors, infractions will be eligible for expunction from a person’s official records as long as the charges were dismissed or for which a finding of not guilty was entered. Also, it will no longer be required that the person had not previously been convicted of a felony.
- Dismissals or findings of not guilty of felonies, misdemeanors, or infractions on or after December 1, 2021, will be expunged by operation of law, not requiring a petition.
- More than one conviction of non-violent misdemeanors can be expunged after a seven-year waiting period.
The team at Collins Law Firm has been handling scores of expunctions for over 20 years in New Hanover County, Pender County, and Brunswick County. If you are interested in having your record expunged, please give our office a call at (910) 793-9000 for a confidential consultation to discuss your eligibility.
PS.: On June 25, 2020, Governor Roy Cooper signed Senate Bill 562.
By Jana H. Collins





 It happens so easily—one makes a bad choice, gets misunderstood, or falsely accused, and in the result faces criminal charges. Regardless of the outcome in a criminal matter—even in case of a wrongful criminal charge—the fact that one was criminally charged will result in a criminal record. Unless dealt with appropriately, a criminal record may create a virtuous circle and negatively affect one’s chances in the job market, in college applications, on the housing market, etc. In an attempt to mitigate or avoid negative consequences of one’s criminal record, one should consult with an attorney about whether or not they are eligible for an expunction of their criminal record and if eligible, pursue the expunction.
It happens so easily—one makes a bad choice, gets misunderstood, or falsely accused, and in the result faces criminal charges. Regardless of the outcome in a criminal matter—even in case of a wrongful criminal charge—the fact that one was criminally charged will result in a criminal record. Unless dealt with appropriately, a criminal record may create a virtuous circle and negatively affect one’s chances in the job market, in college applications, on the housing market, etc. In an attempt to mitigate or avoid negative consequences of one’s criminal record, one should consult with an attorney about whether or not they are eligible for an expunction of their criminal record and if eligible, pursue the expunction.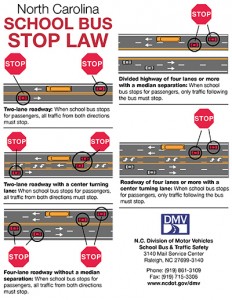 This week, many North Carolina children said goodbye to their summer break and began the 2016-2017 school year. For many students, this involves riding a school bus to and from school. There are thousands of school buses traveling North Carolina highways daily, which means that it is incredibly important for drivers to pay attention to the road and avoid distractions in order to keep everyone safe.
This week, many North Carolina children said goodbye to their summer break and began the 2016-2017 school year. For many students, this involves riding a school bus to and from school. There are thousands of school buses traveling North Carolina highways daily, which means that it is incredibly important for drivers to pay attention to the road and avoid distractions in order to keep everyone safe. The FBI is now more serious than ever about animal cruelty and the consequences associated against these crimes. As of January 1st of this year, the FBI will now collect data on animal cruelty crime through the National Incident-Based Reporting System (NIBRS). Animal cruelty will be classified as a Class A felony, treated as crimes such as homicide, arson, and assault. There will be four categories in which animal abuse crimes can be filed: simple or gross neglect, intentional abuse and torture, organized abuse (i.e., dog fighting), and animal sexual abuse.
The FBI is now more serious than ever about animal cruelty and the consequences associated against these crimes. As of January 1st of this year, the FBI will now collect data on animal cruelty crime through the National Incident-Based Reporting System (NIBRS). Animal cruelty will be classified as a Class A felony, treated as crimes such as homicide, arson, and assault. There will be four categories in which animal abuse crimes can be filed: simple or gross neglect, intentional abuse and torture, organized abuse (i.e., dog fighting), and animal sexual abuse. The North Carolina case Britt v. North Carolina serves as a breakthrough precedent for North Carolinians who lost their right to bear arms due to felony charges. In 1979, Barney Britt plead guilty to PWISD methaqualone (possession with intent to sell and deliver–a central nervous system depressant). He was sentenced to 4 months in prison and probation thereafter. At the end of his sentence in 1987, Mr. Britt’s rights as a North Carolina citizen were fully restored, including the right to bear arms. In 2004, N.C.G.S. §14-415.1 declared it unlawful for any felon to bear any type of firearm despite their reason. Britt sued the state arguing that this new law was unconstitutional. After several hearings and appeals, his case was taken to the Supreme Court where the jury ruled in Britt’s favor. Arguably, Britt served his sentence as a convicted nonviolent felon, and 30 years later had not committed any crime despite that he possessed firearms. Ultimately, Britt had “affirmatively demonstrated that he is not among the class of citizens who pose a threat to public peace and safety” and therefore, a regulation that prohibited him from possessing a firearm could not be “fairly related to the preservation of public peace and safety.”
The North Carolina case Britt v. North Carolina serves as a breakthrough precedent for North Carolinians who lost their right to bear arms due to felony charges. In 1979, Barney Britt plead guilty to PWISD methaqualone (possession with intent to sell and deliver–a central nervous system depressant). He was sentenced to 4 months in prison and probation thereafter. At the end of his sentence in 1987, Mr. Britt’s rights as a North Carolina citizen were fully restored, including the right to bear arms. In 2004, N.C.G.S. §14-415.1 declared it unlawful for any felon to bear any type of firearm despite their reason. Britt sued the state arguing that this new law was unconstitutional. After several hearings and appeals, his case was taken to the Supreme Court where the jury ruled in Britt’s favor. Arguably, Britt served his sentence as a convicted nonviolent felon, and 30 years later had not committed any crime despite that he possessed firearms. Ultimately, Britt had “affirmatively demonstrated that he is not among the class of citizens who pose a threat to public peace and safety” and therefore, a regulation that prohibited him from possessing a firearm could not be “fairly related to the preservation of public peace and safety.” Generally, the fact that one was charged with a crime remains on their record regardless of the disposition of the charge, unless the charge gets expunged. An expungement in North Carolina is the eradication of one’s criminal record by court order. The effects of an expunction or expungement are outlined in N.C.G.S. § 15A-153 and include that upon expunction one may truthfully and without committing perjury or false statement deny or refuse to acknowledge that the criminal incident occurred.
Generally, the fact that one was charged with a crime remains on their record regardless of the disposition of the charge, unless the charge gets expunged. An expungement in North Carolina is the eradication of one’s criminal record by court order. The effects of an expunction or expungement are outlined in N.C.G.S. § 15A-153 and include that upon expunction one may truthfully and without committing perjury or false statement deny or refuse to acknowledge that the criminal incident occurred.